Medium industries in Malaysia have capital investments which are in between light and heavy industries.
A buffer zone, which is the area or distance between industries and residential areas, is introduced to distance the residential area from the area of activity to reduce the exposure to pollution.
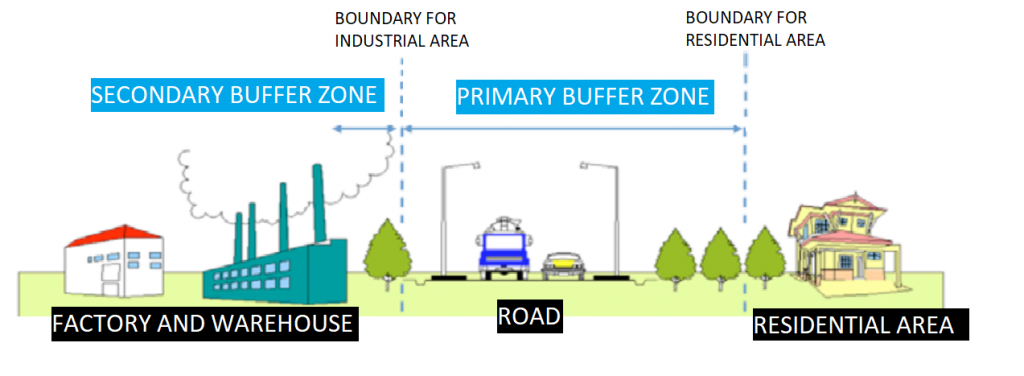
Figure 1: Buffer Zone between Industrial Area and Residential Area
The buffer zones vary based on the specific activity carried out in the industry itself. Below are some examples of a few general activities which can be categorized under the Medium Industry. There will be overlapping of activities of light, medium and heavy industries but the categorisations are mainly based on the scale of the activity itself.
| No | Description |
| 1. | Animal Production Raising domesticated animals, operation of worm farms, beekeeping, etc. |
| 2. | Other Mining and Quarrying Extraction and dredging of industrial sand |
| 3. | Manufacture of Food Products Manufacture vegetables, animal fats, grain mill products, and starch products Production of pulled wool, feathers and down |
| 4. | Manufacture of Beverages Manufacture of malts and distilling, rectifying and blending of spirits |
| 5. | Manufacture of Textiles Preparation and spinning textile fibers Manufacture of textiles, cordage, rope, twine, and netting |
| 6. | Manufacture of Wood and of Products of Wood and Cork, except Furniture; Manufacture of Articles of Straw and Plaiting Materials Manufacture wooden containers and builders’ carpentry |
| 7. | Manufacture of Paper and Paper Products Manufacture pulp, paper and paperboard, and corrugated paper |
| 8. | Manufacture of Chemicals and Chemical Products Manufacture basic chemicals, dye, printing ink, soaps, and printing ink Manufacture gelatins, photographic plate, matches, and man-made fiber |
| 9. | Manufacture of Rubber and Plastic Products Manufacture rubber tyres, synthetic rubber, and processing plastic resins into intermediate or final products. |
| 10. | Manufacture of Other Non-Metallic Mineral Products Manufacture of glass and glass products, clay building materials and porcelain |
| 11. | Manufacture of Basic Metals Manufacture of basic precious and non-ferrous metals. Casting of tubes and pipes, seamless tubes and pipes of steel. |
| 12. | Manufacture of Fabricated Metal Products, except Machinery And Equipment Manufacture structural metal products, weapons and ammunition, and fabricated metal products |
| 13. | Manufacture of Electrical Equipment Manufacture of batteries, wiring and wiring devices and lighting equipment. |
| 14. | Manufacture of Machinery and Equipment n.e.c Manufacturing general-purpose machinery, fluid power equipment, lifting and handling equipment and special-purpose machinery |
| 15. | Manufacture of Motor Vehicles, Trailers and Semi-Trailers |
| 16. | Manufacture of Other Transport Equipment Building of ships and boats, transport equipment and motorcycles. |
| 17. | Manufacture of Furniture Manufacture of furniture |
| 18. | Repair and Installation of Machinery Equipment Repair fabricated metal products, machinery and equipment and repair and maintenance of division 30 transport equipment. |
| 19. | Electricity, Gas, Steam and Air Conditioning Supply Electric power generation, transmission and distribution. Production, collection and distribution of steam and hot water. |
| 20. | Sewerage Operation of sewer systems of sewage treatment facilities |
A primary buffer zone is an area or distance which is located outside the designated area for the project or proposed activity. The medium industry has a buffer zone that has the size which is smaller than the heavy industry and larger than the light industry. The table shown below shows the criteria for an industry to be considered as light industry and the minimum buffer zone for it:
| Category | Industry/Activity Description | Primary buffer zone requirement |
| Medium |
Moderate
pollution potential and risk due to fire, explosion, and/or
hazardous chemicals
Moderate
air pollution potential (including odour) from low levels of
residual air pollutants
Moderate
potential for emission of greenhouse gases and/or ozone depleting
substances
Moderate
noise and/or vibration with no significant residual impact
Generate
significant quantities of wastewater containing low levels of
residual pollutants Generate scheduled wastes which are mostly
readily treated or managed within prescribed facilities.
| Greater or equal to 150 m. Buffer distance for specific processes or polluting sources which are difficult to control effectively may require greater buffer distances. Actual buffer is to be determined by modeling studies where necessary. |
If it is unsure whether the activity planned falls under Light, Medium or Heavy industry, the Department of Environment (DOE) should be consulted for further information. A professional engineer could also be consulted so that a proper buffer zone can be assigned to avoid future complications.
Disclaimer: The information above is only extra references to “Guidelines for Siting and Zoning of Industrial and Residential Areas” as published by the Department of Environment (DOE). We do not take any responsibility and not liable for any misunderstandings, loss, and damages caused by the information above. Kindly consult the Department of Environment (DOE) for more detailed information.
Ir. Dr. Justin LAI Woon Fatt
CEO/ Founder
IPM Group
Reference:
1. Department of Environment. (2019). GUIDELINES FOR SITING AND ZONING OF INDUSTRY AND RESIDENTIAL AREAS (2nd ed., p. 134). Retrieved from http://www.doe.gov.my/eia/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/Guidelines-For-Siting-and-Zoning-of-Industry-and-Residental-Areas-2012.pdf
