Heavy industries in Malaysia are different from light industries in the sense that heavy industries are usually more capital intensive compared to light or medium industries; which means they require a lot of machinery and equipment.
A buffer zone, which is the area or distance between industries and residential areas, is introduced to distance the residential area from the area of activity to reduce the exposure to pollution.
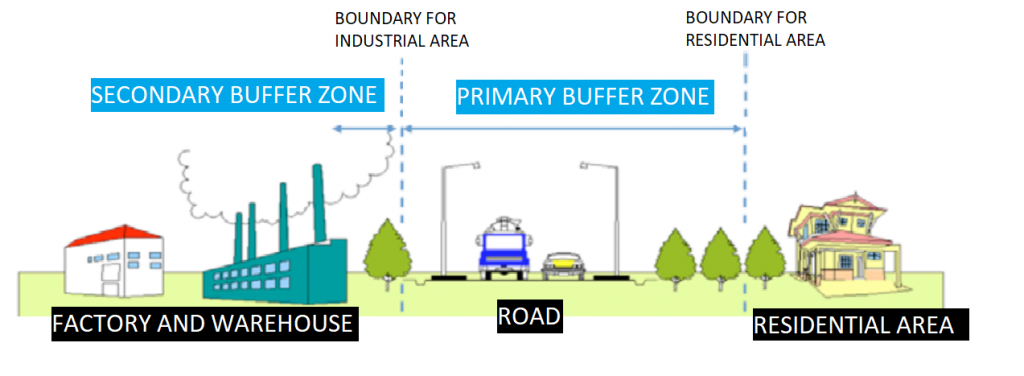
Figure 1: Buffer Zones between Industrial Area and Residential Area
The buffer zones vary based on the specific activity carried out in the industry itself. Below are some examples of a few general activities which can be categorized under the Heavy Industry. There will be overlapping of activities of light, medium and heavy industries but the categorisations are mainly based on the scale of the activity itself.
| No | Description |
| 1. | Animal Production Raising of farm animals including racing horses and other equines |
| 2. | Mining and Quarrying Mining coal, lignite, iron ore, bauxite, gold, etc |
| 3. | Extraction of Crude Petroleum and Natural Gas Extraction of crude petroleum including extraction and onsite processes. Extraction of natural gas |
| 4. | Mining of Metal Ores Mining metal ores other than uranium and thorium |
| 5. | Other Mining and Quarrying Mining and quarrying Quarrying stone such as marble granite sandstone, etc |
| 6. | Mining Support Service Activities Support activities for petroleum and natural gas extraction Support activities for mining and quarrying |
| 7. | Manufacture of Food Products Processing and preserving meats, fish, crustaceans and molluscus Production of hides and skin and animal offal. Operation of animal slaughterhouse |
| 8. | Manufacture of Textiles Spinning, weaving, and finishing of textiles Preparation and spinning of textile fibers. |
| 9. | Manufacture of Leather and Related Products Tanning and dressing of leather; dressing and drying of fur |
| 10. | Manufacture of Wood and of Products of Wood and Cork, except Furniture; Manufacture of Articles of Straw and Plaiting Materials Sawmilling and planning of wood Manufacture of products of wood, cork, straw and plaiting materials |
| 11. | Manufacture of Paper and Paper Products Manufacture of pulp, paper, and paperboard Manufacture of bleached, semi-bleached or unbleached paper pulp by mechanical, chemical or semi-chemical process from virgin wood |
| 12. | Manufacture of Coke and Refined Products Manufacture of coke and oven products Manufacture of refined petroleum products |
| 13. | Manufacture of Chemicals and Chemical Products Manufacture of basic chemicals Manufacture of organic and inorganic chemicals except for nitric acid |
| 14. | Manufacture of Rubber and Plastic Products Manufacture of rubber tyres and tubes |
| 15. | Manufacture of Other Non-metallic Mineral Products Manufacture of glass, cement, lime, clinkers, and refractory products. |
| 16. | Manufacture of Basic Metals Manufacture of basic iron and steel Operation of the blast furnace, steel converters |
| 17. | Manufacture of Fabricated Metal Products, except Machinery and Equipment Manufacture of structural metal products, tanks, weapons, ammunition. Forging, pressing, stamping and roll-forming of metal |
| 18. | Manufacture of Other Transport Equipment Building ships and boats, railway locomotives, air and spacecraft machinery and military fighting devices. |
| 19. | Electricity, Gas, Steam and Air Conditioning Supply Electric power generation, transmission and distribution Manufacture of gas; distribution of gaseous fuels through mains |
| 20. | Waste Collection, Treatment, and Disposal Activities; Materials Recovery Waste treatment and disposal Treatment of waste |
A primary buffer zone is an area or distance which is located outside the designated area for the project or proposed activity. The table shown below shows the criteria for an industry to be considered as heavy industry and the minimum primary buffer zone for it:
| Category | Industry/Activity Description | Primary buffer zone requirement |
| Heavy | High pollution potential and risk due to fire, explosion, radiation, and/or highly hazardous chemicals. High air pollution potential (including odour) from residual pollutants in air emissions (fugitive and source emissions). High potential for the emission of greenhouse gases and/or ozone-depleting substances. Excessive noise and/or vibration exceeding safe limits. Generate large quantities of wastewater containing significant levels of residual pollutants. Use large quantities of raw materials with the potential to cause significant fugitive emissions during handling, transfer and storage. Generate significant amounts of scheduled wastes that are difficult to treat or manage. | Greater or equal to 300 m. Buffer distance for specific processes/polluting sources that are difficult to control effectively may require greater buffer distances. The actual buffer is to be determined by modeling studies. |
If it is unsure whether the activity planned falls under Light, Medium or Heavy industry, the Department of Environment (DOE) should be consulted for further information. A professional engineer could also be consulted so that a proper buffer zone can be assigned to avoid future complications.
Disclaimer: The information above is only extra references to “Guidelines for Siting and Zoning of Industrial and Residential Areas” as published by the Department of Environment (DOE). We do not take any responsibility and not liable for any misunderstandings, loss, and damages caused by the information above. Kindly consult the Department of Environment (DOE) for more detailed information.
Ir. Dr. Justin LAI Woon Fatt
CEO/ Founder
IPM Group
Reference:
1. Department of Environment. (2019). GUIDELINES FOR SITING AND ZONING OF INDUSTRY AND RESIDENTIAL AREAS (2nd ed., p. 134). Retrieved from http://www.doe.gov.my/eia/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/Guidelines-For-Siting-and-Zoning-of-Industry-and-Residental-Areas-2012.pdf
